The project is drone assembling, onboard programming, implementation of an AI-based model for autonomous drone operation, and integration. The development of an Android mobile application for managing drone settings to perform combat missions is also a part of this project.
AI Drones
The project is drone assembling, onboard programming, implementation of an AI-based model for autonomous drone operation, and integration. The development of an Android mobile application for managing drone settings to perform combat missions is also a part of this project.
Solution
Chudovo’s embedded & computer vision team worked on the drone system, where the main logic and intelligence run live on the drone, and the mobile application serves as an interface for setting parameters and commands. Main highlights for on-board focused drone programming:
- The first stage involved assembling drones from scratch with the necessary hardware configuration
- Flight controller layer – Ardupilot (runs in C++ and communicates via MAVLink)
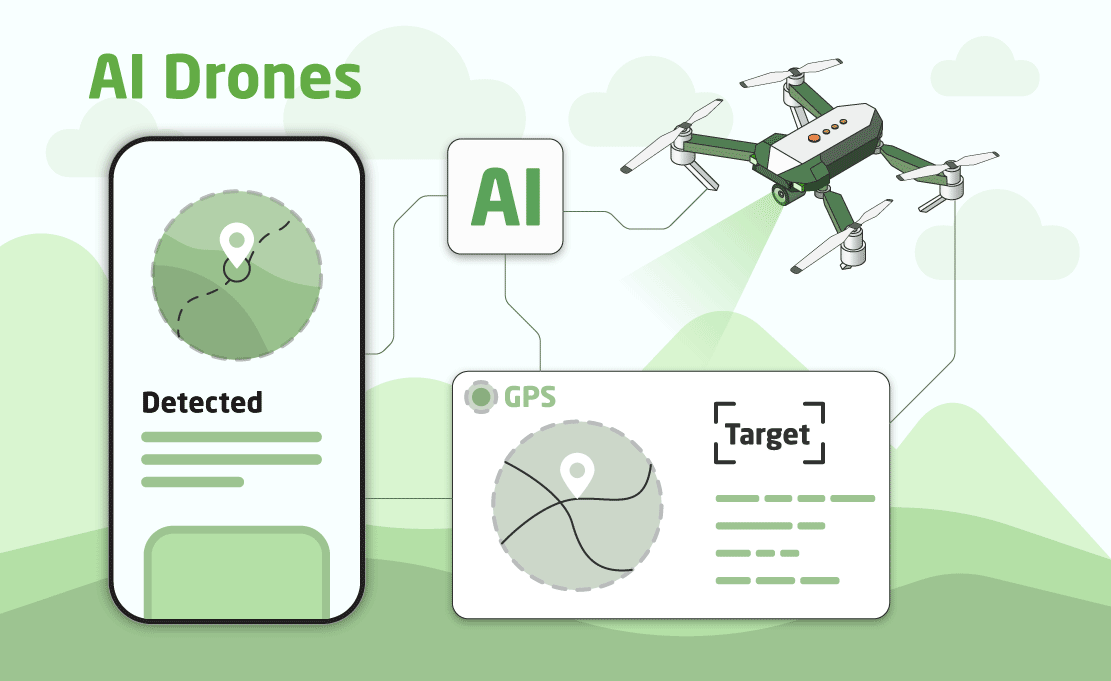
- AI-powered module (Yolo + Python) is running on the onboard Linux computer – Raspberry Pi, which communicates with the camera, flight controller, and Android app via Bluetooth
- Mobile Kotlin application serves as a control panel and uses the Bluetooth SDK to connect to the onboard Linux
The AI drones work in the following way:
- The AI-capable drone is programmed at the start via a mobile application
- The operator sets the departure region and the search radius of the drone, and also prioritizes targets (for example, infantry, cars, tanks, artillery)
- The AI drone flies along the route set by the operator (the operator sets the end point or several points to be flown around)
- The AI drone takes off and flies along the route, searching for targets in the given region
- Depending on the goal, which is also set via the application, it performs the task. The mission can be either landing at a given point or dropping or hitting an object at a given point, or search + hitting.
- This happens with the help of GPS and without GPS (if without it, an inertial navigation system based on the sensors: compass, IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit), barometer, rangefinders, and camera). In flight mode without GPS, the drone is not affected by electronic warfare (EW).
- The main movement of the AI-powered drone is based on a camera, which transmits information to the processor, where details of the surrounding environment are recognized
- The AI drone can perform tasks at different altitudes, in different weather conditions, and is equipped with an obstacle avoidance option
- The drone can perform the tasks as an FPV managed by an operator or an AI drone managed by artificial intelligence
- Drones can strike with precision at a range of 20 kilometers
Mobile application for managing artificial intelligence drones and missions includes the following scopes of features:
- Authorization authentication
- A directory with a list of connected drones (includes the characteristics of each drone).
- Adding/editing/deleting drones
- Module for setting a route for the combat missions by manually entering coordinates or selecting zones on the map
- Route settings with characteristics
- Drone testing mode
- Drone operation logs
- Ability to cancel a mission via the application
Chudovo team composition on the AI drones project:
- Software engineer for Python/Unix (drone level)
- Software engineer with Python and Android/Kotlin know-how
- AI developer
- Engineer for assembly, soldering, and testing
All the engineers have embedded development experience.